AI Adoption in Financial Advisory: Portfolio Explanations, Investment FAQs & Retirement Planning
Executive Summary
The financial-advisory sector is undergoing rapid transformation driven by large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT. Consumers already use AI for investment questions, portfolio clarification, and retirement planning, while financial advisors themselves are adopting LLMs as co-pilots for planning, explanations, and client engagement.
This whitepaper compiles findings from eight authoritative articles across universities, industry giants, consulting firms, regulatory bodies, and financial publishers. The evidence shows:
AI is becoming a primary financial guidance tool for younger generations.
ChatGPT is now used for real financial decision-making, including product comparison and portfolio analysis.
Retirement planning is a high-value LLM application, with global institutions adopting AI for plan personalization and risk modeling.
Both benefits and risks exist: while AI improves clarity and access, poor prompt framing or blind trust can lead to financial loss.
Financial-advisory teams must design structured, compliant AI workflows to leverage its upside safely.
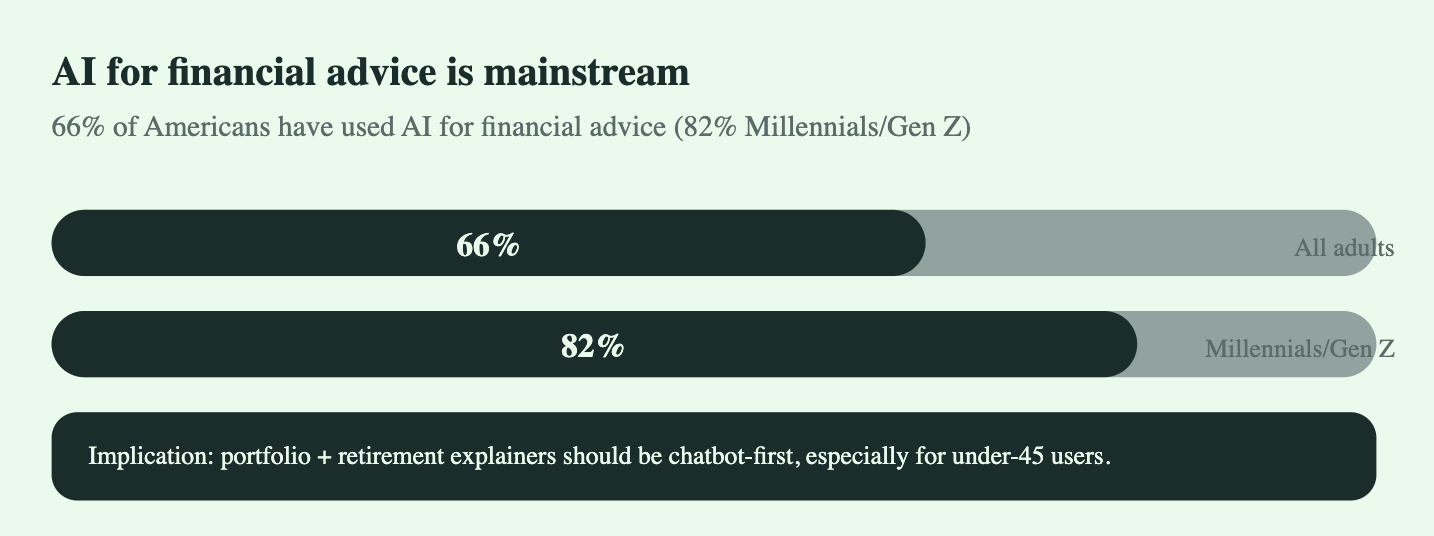
66% of Americans say they’ve used AI to seek financial advice (e.g., budgeting, investing, retirement), with 82% among Millennials/Gen Z.
54% of Americans have asked ChatGPT about financial products/services, and 47% have used it for investment advice.
Surveys cited in Reuters show 13% of investors already use AI tools for portfolio decisions; about 1 in 10 retail investors use chatbots for stock selection.
A SmartAsset survey reports 60% of financial advisors either use or are interested in using ChatGPT in client advisory workflows.
1. Market Context & User Behavior
1.1 Consumers Are Already Using AI for Financial Guidance
Across multiple surveys, AI has become a mainstream personal-finance tool:
Majority of adults have used AI for financial questions.
Millennials and Gen Z treat AI as their first stop for budgeting, investment rationale, ETF breakdowns, and retirement tasks.
ChatGPT is the most frequently used AI assistant for money-related queries.
The implication is clear:
Consumers expect on-demand, conversational, personalized explanations—not long PDFs, web articles, or dense prospectuses.
1.2 ChatGPT as a Financial Decision-Making Engine
Users engage ChatGPT to:
Explain investment products (ETFs, SIPs, mutual funds, REITs)
Compare options (index fund vs. active fund)
Break down portfolio allocations
Estimate retirement needs
Interpret risk, returns, fees, and diversification
Clarify jargon (expense ratio, beta, duration, etc.)
This is no longer a “toy use-case.”
People rely on LLMs for advice-adjacent decisions, often affecting real money.
1.3 Risks Identified in Consumer Behavior
Investopedia found:
Nearly 1 in 5 users lost $100+ after following unverified AI advice.
Reasons include:
AI misunderstanding personal context
Users assuming AI is a certified advisor
Calculation or assumption errors
Lack of disclosure or disclaimer awareness
This highlights the need for controlled, professional-grade AI systems inside firms—not ungoverned public model usage.
2. Insights From Key Industry Sources
Below is a synthesized breakdown of insights from the 8 articles.
2.1 Gies College of Business – Can ChatGPT Give Good Financial Advice?
Key takeaway:
ChatGPT produces understandable, well-structured financial guidance but struggles with prioritization, context understanding, and edge-case calculations.
Implications:
LLMs excel at explanations, not decisions.
Guardrails, templates, and validation layers are essential.
Perfect for portfolio explanations, scenario breakdowns, and FAQs.
2.2 BlackRock – AI Revolution in Retirement
Key takeaway:
AI is improving retirement planning with:
Personalized plan design
Participant engagement
Real-time investment education
Automated reasoning for choices
Implications:
Enterprise financial institutions see LLMs as a strategic differentiator in customer experience.
2.3 World Economic Forum – Modernizing Pension Systems with AI
Key takeaway:
AI can help mitigate the global retirement crisis via:
Adaptive contribution planning
Cost-controlled pension models
Real-time risk monitoring
Personalized communication
Implications:
Retirement systems are shifting from static documentation to dynamic, conversation-driven explanations.
2.4 Britannica – AI for Retirement & Financial Planning
Key takeaway:
AI helps consumers:
Set retirement goals
Estimate savings requirements
Model “what if” scenarios
Explore investment options with clarity
Implications:
Huge consumer demand for LLM-based retirement explainers.
2.5 Investopedia – 1 in 5 Lost Money Using AI Advice
Key takeaway:
Over-reliance on unregulated AI leads to loss.
Many users treat ChatGPT as a certified advisor.
Errors occur in calculations, assumptions, and risk interpretations.
Implication:
Financial firms must build safe AI layers—validated, compliant, and branded—because if they don’t, users will rely on public ChatGPT anyway.
2.6 Harvard Business School – Does AI Help Investors?
Key takeaway:
AI produces rational, structured financial guidance—but investors may misinterpret tone as authoritative.
Implications:
Models should be configured to:
Express uncertainty clearly
Provide factual breakdowns
Avoid unverified recommendations
Include compliance disclaimers
2.7 Mercer – AI & Retirement Plans
Key takeaway:
AI improves:
Benefit communication
Investment route selection
Lifetime income modeling
Macro–micro alignment of retirement portfolios
Implication:
Retirement benefits teams can deploy AI-driven onboarding, education, and planning.
2.8 FinTech Weekly – Optimizing 401(k)s with AI
Key takeaway:
AI changes 401(k) planning from static to dynamic:
Personalized
Data-driven
Updated continuously
Based on market signals and life milestones
Implication:
401(k) providers can deploy conversational bots for ongoing participant engagement.
3. Strategic Opportunities for Firms
3.1 Portfolio-Explanation Engines
LLMs excel at:
Explaining asset allocation
Interpreting risk vs reward
Clarifying fees, ratios, and comparisons
Breaking down historical performance
Translating complex financial jargon into simple language
This is one of the strongest high-value AI use cases.
3.2 Investment FAQ Assistants
Top queries users ask:
“Which is better: index fund or active fund?”
“What is a good expense ratio?”
“Is SIP better than lump sum?”
“Explain this ETF.”
“Why is my portfolio down this month?”
Firms can automate:
FAQ handbooks
Product comparison tools
Prospectus explainers
Risk-profile education flows
3.3 Retirement Planning Co-Pilot
High demand exists for:
Personalized retirement projections
Income-replacement walkthroughs
Social-security integration
Tax-efficient withdrawal strategies
Scenario simulations
AI enables “always-on financial planning.”
3.4 Compliance-Safe Advisor Tools
Advisors themselves want AI to:
Draft explanations
Summarize product options
Create retirement-plan narratives
Prep client reports
Answer routine questions faster
This frees advisors to focus on relationship building, not paperwork.
4. Risk, Governance & Compliance Considerations
4.1 Key risks
Inaccurate numerical assumptions
False confidence tone
Hallucinated facts or data
Users misinterpreting content as licensed advice
Non-compliance with local regulations (FINRA, SEC, FCA, etc.)
4.2 Governance requirements
Firms should implement:
Model guardrails: restricted instructions, disclaimers
Human-in-loop architecture for sensitive topics
Template-based outputs
Logging for audits
Knowledge-grounding using firm-approved content
Scenario-testing for high-risk prompts
4.3 Risk-reduction approaches
Validate numbers with deterministic calculators
Provide multiple-option outputs, not prescriptive directions
Ensure disclaimers are always included
Limit equity-specific recommendations
5. The Future of AI in Financial Advisory (2025–2030)
5.1 Hyper-personalized advisory
Every client receives:
Customized portfolio explanations
Daily insights on their allocation
Real-time reasoning for market shifts
5.2 Integrated retirement ecosystems
AI merges:
Spending data
Savings history
Market predictions
Longevity estimates
to create holistic retirement journeys.
5.3 AI-powered advisory firms
The industry will split into:
Advisor-led companies using AI → efficiency + trust
AI-led companies with advisors → scale + cost advantage
Both models can coexist.
5.4 Regulation will formalize AI advice
Expect new rules around:
AI disclosures
Reasoning transparency
Investment-advice boundaries
Data validation layers
Model certification
6. Conclusion
AI is no longer “experimental” in financial advisory—it is now central to how consumers learn, plan, and make decisions. The eight articles reviewed converge on a single message:
LLMs like ChatGPT are transforming portfolio explanations, investment education, and retirement planning into a dynamic, personalized, conversational experience.
Financial firms that integrate AI early will gain a competitive edge in:
Customer satisfaction
Advisor productivity
Operational efficiency
Regulatory preparedness
Long-term trust building
Those who wait will face an uphill battle as consumers increasingly choose AI-first financial guidance.